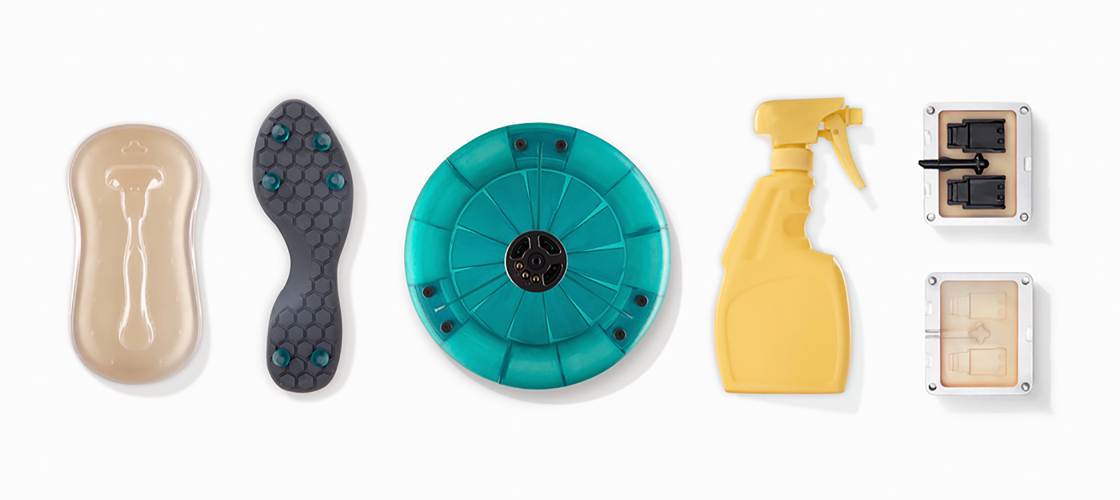
What is SLA 3D printing?

SLA stands for stereolithography, and it is sometimes abbreviated as just SL. As the name suggest, SLA 3D printing is a method of additive manufacturing where a prototype, model or functional part can be 3D printed through a process known as vat photopolymerization.
Although all these terms that describe this 3D printing technology may sound like something extraordinarily new, SLA is consider the father of additive manufacturing processes, as it is the oldest 3D printing method with a patent filed by the founder of 3D Systems, Chuck Hull, back in 1986.
How does SLA 3D printing work?
The basic working principle for the SLA 3D printing process is to produce a solid polymer by means of a photochemical process. In simple words, a liquid resin is cured by a source of light until it becomes a solid plastic. The source of light in SLA 3D printers is usually a UV laser beam which can be controlled to cure the resin layer by layer to achieve the desired results.
As it might be expected, the materials used in SLA 3D printing are resins known as liquid photopolymers which are thermoset materials susceptible to react to active light.
For a more comprehensive view of the process, let’s take a look at the parts and steps involved in SLA 3D printing:
1. The liquid resin is poured in a tank with the build platform positioned inside the tank at a distance equal to the height of one layer from the surface of the liquid.
2. By using the information translated from the CAD model, the software of the printer focuses the laser beam in the correct path using a group of mirrors called galvanometers or just galvos. Then, following that path, the laser selectively curates the resin and solidifies it to create the corresponding layer which represents a cross section of the model.
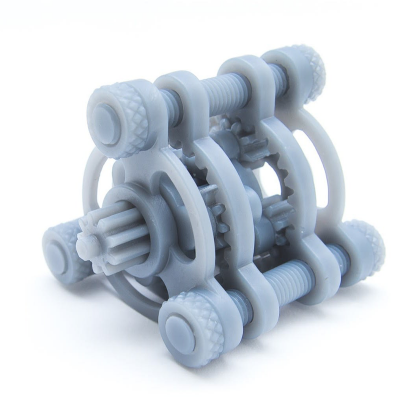
3.After the layer is completely solid, depending on the design of the printer, the platform is moved up or down by means of an elevator and a sweeper blade recoats the surface for the new layer. These steps repeat until the part is completed.
4.Depending on the specific requirements for the part printed, post processing may be required. The minimum post process steps involve cleaning the surface to remove any resin that has been left uncured. This cleaning is usually done with isopropyl alcohol. Other post process requirements include: post curing to improve strength, removing supports, machining, painting, assembling, among others.

What are the advantages of SLA 3D printing?
SLA 3D printing stands out in some aspects when compared to other 3D printing technologies. Some of the advantages of SLA 3D printing are:
1. It is considered the most precise 3D printing method in the current market.
2.Prototypes and functional parts can be printed to a high quality while covering complex shapes and special features.
3. Some manufacturers claim that layer thickness can be as low as 25 μm.
4. Smooth surface finish.
5. It is suitable for large parts.
6. Watertightness can be achieved.
What are the drawbacks of SLA 3D printing?
As it happens with any technology, there are some possible disadvantages or drawbacks to consider when choosing SLA 3D printing as your additive manufacturing method. The most important are:
1. SLA 3D printing can be slower than other 3D printing methods.
2. Some details of the part like slopes and overhangs may require support structures during the printing process.
3. Compared to other materials like hard thermoplastics, some resins can be fragile which could be a problem for functional parts or mechanical testing.
4. Materials may be difficult to exchange between printers, as some manufacturers have proprietary resins that only work on their machines.
5. Initial investment may be higher compared to other methods like FDM 3D printing.
As you can see, SLA 3D printing can satisfy very specific requirements, especially those of tolerance, complex and fine details or high-quality and smooth surface finishes. However, if you are not completely sure this is the best method for you, the recommendation is to consult with an expert to avoid undesired failures and reduce costs related to repeated work in trial an error.